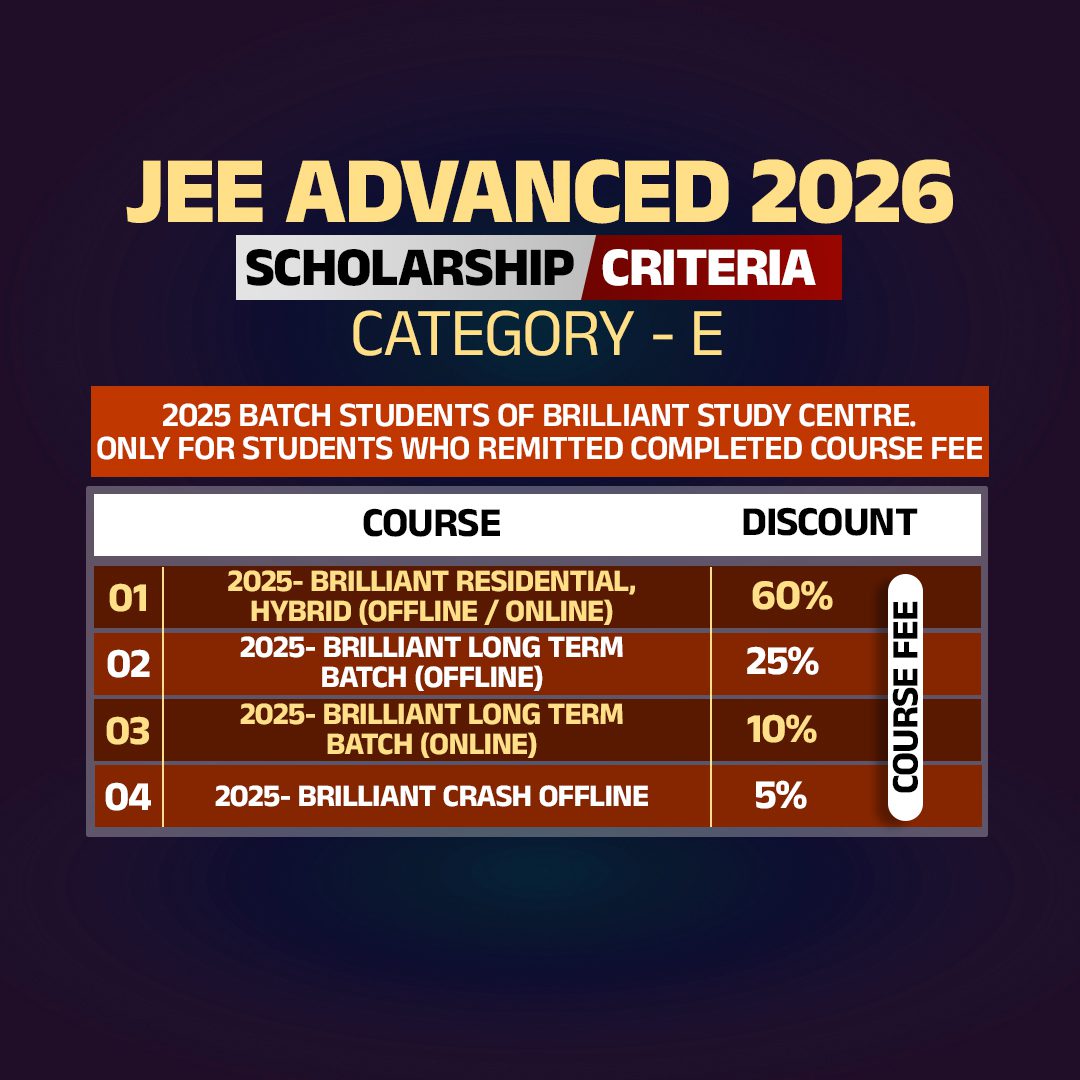
Jee Scholarship
Jee Scholarship - Until java ee 7 only ejb was transactional and the @transactional annotation didn't exist. For example, tomcat, a jee compliant web container is, arguably, a jse application as it only needs the jre to run, even though it implements a portion of jee. I realize that literally it translates to java enterprise edition. I just want to use a definition of an code authorisation flow for oidc and then use the fetched and validated access token. I tried a lot of things for pac4j but i'm feeling a bit lost. 0 i want to create a jee web app with intellij community edition, so i want to learn about servlets and jsp and i have intellij community edition and i want to know if i could create a jee web. I do not understand the differences between jee, j2ee, jse, jme and jdk. But what i'm asking is what does this really mean? It is said that in the spring javadoc article about drivermanagerdatasource class, that this class is very simple and that it is recommended to use a jndi datasource provided by the container. For what i do need this stuff? I do not understand the differences between jee, j2ee, jse, jme and jdk. I realize that literally it translates to java enterprise edition. It’s a component based approach to develop web app. It is said that in the spring javadoc article about drivermanagerdatasource class, that this class is very simple and that it is recommended to use a jndi datasource provided by the container. I just want to use a definition of an code authorisation flow for oidc and then use the fetched and validated access token. For what i do need this stuff? Since java ee 7 and jta 1.2 you can use transactional interceptor in cdi with. For example, tomcat, a jee compliant web container is, arguably, a jse application as it only needs the jre to run, even though it implements a portion of jee. Until java ee 7 only ejb was transactional and the @transactional annotation didn't exist. I tried a lot of things for pac4j but i'm feeling a bit lost. I found this shortcuts while learning about java. For example, tomcat, a jee compliant web container is, arguably, a jse application as it only needs the jre to run, even though it implements a portion of jee. I just want to use a definition of an code authorisation flow for oidc and then use the fetched and validated access token.. It is said that in the spring javadoc article about drivermanagerdatasource class, that this class is very simple and that it is recommended to use a jndi datasource provided by the container. 0 i want to create a jee web app with intellij community edition, so i want to learn about servlets and jsp and i have intellij community edition. I realize that literally it translates to java enterprise edition. For example, tomcat, a jee compliant web container is, arguably, a jse application as it only needs the jre to run, even though it implements a portion of jee. I tried a lot of things for pac4j but i'm feeling a bit lost. It is said that in the spring. 0 i want to create a jee web app with intellij community edition, so i want to learn about servlets and jsp and i have intellij community edition and i want to know if i could create a jee web. It’s a component based approach to develop web app. I tried a lot of things for pac4j but i'm feeling. I do not understand the differences between jee, j2ee, jse, jme and jdk. For example, tomcat, a jee compliant web container is, arguably, a jse application as it only needs the jre to run, even though it implements a portion of jee. I tried a lot of things for pac4j but i'm feeling a bit lost. Since java ee 7. It’s a component based approach to develop web app. I realize that literally it translates to java enterprise edition. Since java ee 7 and jta 1.2 you can use transactional interceptor in cdi with. When a company requires java ee experience, what are they really asking for? I found this shortcuts while learning about java. I tried a lot of things for pac4j but i'm feeling a bit lost. I realize that literally it translates to java enterprise edition. 0 i want to create a jee web app with intellij community edition, so i want to learn about servlets and jsp and i have intellij community edition and i want to know if i could. I realize that literally it translates to java enterprise edition. Since java ee 7 and jta 1.2 you can use transactional interceptor in cdi with. It is said that in the spring javadoc article about drivermanagerdatasource class, that this class is very simple and that it is recommended to use a jndi datasource provided by the container. I do not. It is said that in the spring javadoc article about drivermanagerdatasource class, that this class is very simple and that it is recommended to use a jndi datasource provided by the container. I found this shortcuts while learning about java. It’s a component based approach to develop web app. When a company requires java ee experience, what are they really. But what i'm asking is what does this really mean? Until java ee 7 only ejb was transactional and the @transactional annotation didn't exist. 0 i want to create a jee web app with intellij community edition, so i want to learn about servlets and jsp and i have intellij community edition and i want to know if i could. I realize that literally it translates to java enterprise edition. I found this shortcuts while learning about java. When a company requires java ee experience, what are they really asking for? I do not understand the differences between jee, j2ee, jse, jme and jdk. It’s a component based approach to develop web app. But what i'm asking is what does this really mean? I tried a lot of things for pac4j but i'm feeling a bit lost. 0 i want to create a jee web app with intellij community edition, so i want to learn about servlets and jsp and i have intellij community edition and i want to know if i could create a jee web. For example, tomcat, a jee compliant web container is, arguably, a jse application as it only needs the jre to run, even though it implements a portion of jee. Since java ee 7 and jta 1.2 you can use transactional interceptor in cdi with. I just want to use a definition of an code authorisation flow for oidc and then use the fetched and validated access token.NEETJEE Scholarship Exam for Grade 11 Students Brilliant Qatar
Top Scholarships for JEE Main 2026 Aspirants Getmyuni
PhysicsWallah Offers Rs 250 Crore Scholarship for JEE, NEET Students in
JEE Advanced Question Paper Brilliantpala
JEE Scholarship 2025, Eligibility, Application and Benefits
JEE Scholarship
Top Scholarships for JEE Main 2025 Aspirants Getmyuni
JEE vs NEET Scholarships, Which is Right for You?
JEE Main Scholarships 2025 Your Guide to Funding Engineering Dreams
Government And Private Scholarships For NEET & JEE Students
Until Java Ee 7 Only Ejb Was Transactional And The @Transactional Annotation Didn't Exist.
It Is Said That In The Spring Javadoc Article About Drivermanagerdatasource Class, That This Class Is Very Simple And That It Is Recommended To Use A Jndi Datasource Provided By The Container.
For What I Do Need This Stuff?
Related Post: